This is an old revision of the document!
- beagleboneblack
- Jonathan Haack
- Haack's Networking
- netcmnd@jonathanhaack.com
To locate device if auto-mounted
sudo dmesg
umount /dev/mmcblk0p1
Optional: use fdisk to remove the partition first before dding … use blkdiscard before
sudo dd of=/dev/mmcblk0 if=/home/sexa/Downloads/bone-debian-9.2-iot-armhf-2017-10-10-4gb.img bs=1M conv=fdatasync [or && sync]
After this, pull out SD card. Plug back in. Locate where it mounted, prepare to edit file to allow it to run the installer upon boot. This is located in boot/enV.txt relative to wherever the media mounted. Eg., cd /media/sexa/rootfs/boot/
cmdline=init=/opt/scripts/tools/eMMC/init-eMMC-flasher-v3.sh
Get out of the directory asap. then:
umount /dev/mmcblk0p1
Now that the image has been turned into an installer, you may put the microSD card into the Beagle Bone (without power).
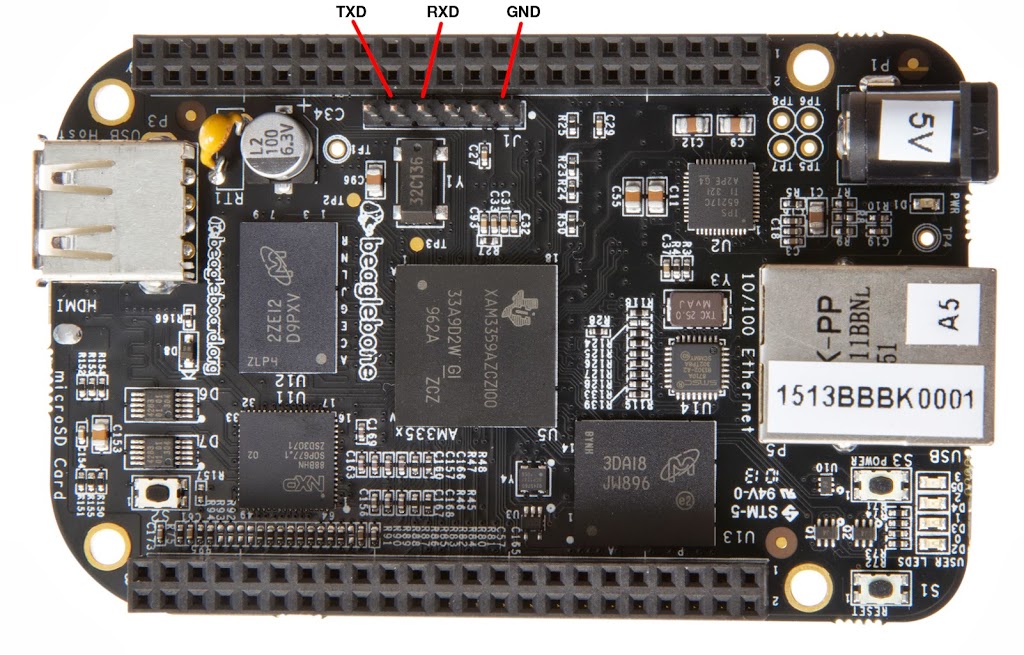
On a typical serial to USB adapter, and almost all others, the colors are white (receive), green (transmit), black (ground), red (5V power). Do not use the red cable unless you know what you are doing. Otherwise, make sure that the adapter's transmit goes to the Beagle's receive, and the adapter's receive to the Beagle's transmit. The diagram below shows the Beagle's perspective. From left to right, there are 6 pins, so it would be : nothing, white, green, nothing, nothing, black. The adapter commonly has a name like ttyUSB0, therefore this command should do the trick:
sudo screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200
Once the Beagle Bone is set up, one can leverage the screen command with ssh to tunnel to another host, and then pass a screen command to keep the commands you initiate persistent on the client you connected to. That syntax looks like this:
ssh -p 222 -t user@host.com screen -DRO
Some other common speeds are 9600, 57600, 38400, 19200. For the Beagle Bone black, I always use 115200. These speeds are in baud.
– – – – – –
This section below is from some revisions I wrote for Jason's beaglebone stripping tutorial …
Clean Up Post-Install
apt-get install screen deborphan ntp
the new version has an ntp server
be sure to fix /etc/network/interfaces before removing connman - uncomment the lines for DHCP for eth0, remove extraneous lines and the manual entry that comes stock with bbb … then connect to the beaglebone with ssh and screen …
ssh -t root@<x.x.x.x> screen -DRO
for i in udhcpd chromium-codecs-ffmpeg-extra connman lximage-qt lxmenu-data pcmanfm-qt qupzilla xserver-xorg-core "light*" chromium-browser nodejs "lxqt*" xserver-common "apache2*" bluez "xfonts*" "x11-*" "x11proto-*" build-essential alsa-utils; do apt-get -y purge $i; done
After this command, the ssh session hung, and we could only access with screen at a different speed of 9600 … but, as long as you took care of /etc/network/interfaces above, then a reboot (worst case) or waiting should bring it back up.
apt-get --purge autoremove
apt-get --purge remove `deborphan` OR [apt-get purge `deborphan`] OR [apt-get purge $(deborphan)]
run deborphan a few times untill all is removed
apt update apt dist-upgrade apt clean
edit /etc/issue.net to remove the goofy ssh splash
cd /var/log && rm lastlog && ln -s /dev/null lastlog cd /etc/cron.daily && mv man-db man-db.disabled [if it exists]
to find latest writes to disk: find / -mount -newermt 14:44:00 [to see what logs are post-updates, i.e., for limiting writes to eMMC]
Verify /etc/fstab configuration, include noatime like this example
FROM FSTAB: UUID=57e4a3f6-7951-40ae-ad25-b445959e1c30 / ext4 noatime,errors=remount-ro 0 1 debugfs /sys/kernel/debug debugfs defaults 0 0
#if we use an external sdcard, we are less concerned with re-writes, so enable the logs on the sdcard (create directories for each location below, mountpoints, etc.)
UUID=eb885f2f-28a4-49a6-99c9-3f8b0b7a871d /sdcard ext4 noatime,nofail,errors=remount-ro 0 2
/sdcard/tmp /tmp none bind,nofail 0 0 /sdcard/var/log /var/log none bind,nofail 0 0 /sdcard/var/lib/mysql /var/lib/mysql none bind,nofail 0 0 /sdcard/var/lib/cacti/ /var/lib/cacti none bind,nofail 0 0 /sdcard/var/lib/ntp /var/lib/ntp none bind,nofail 0 0
End of Jason's stripping tutorial …
– – – – –
This tutorial is a designated “Invariant Section” of the “Technotronic” section of Haack's Wiki as described on the Start Page. This does not include the sections quoted from Jason's tutorial.
— oemb1905 2019/01/13 12:22